Request information
For large buyers or companies it is possible to have price lists with different prices and payment terms.
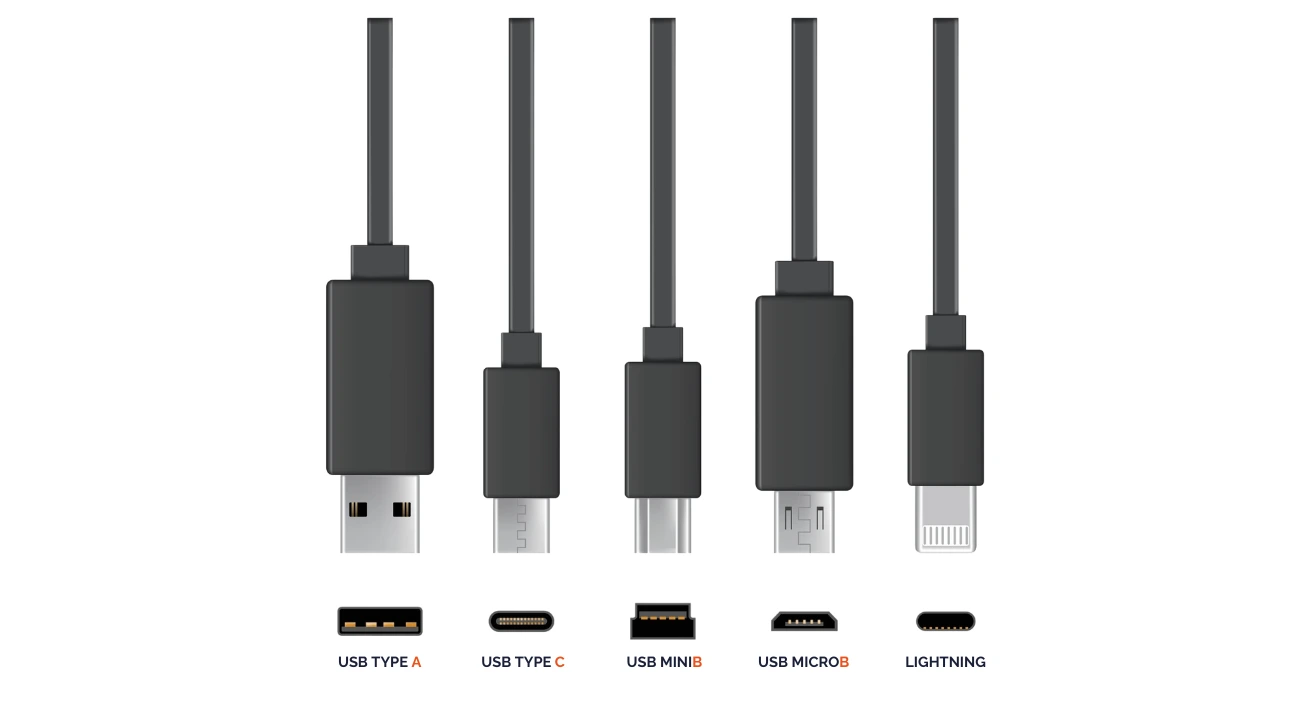
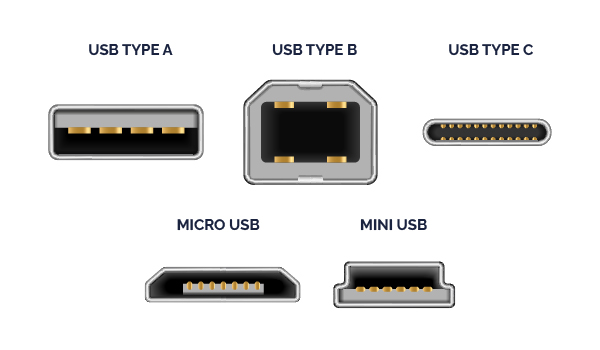
Currently, several types of USB ports and cables are available on the market (USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, and micro-USB), and it's crucial to identify them for the best everyday usage.
This overview will provide the tools to distinguish each type of USB and choose the right one for your needs.
The USB standard (Universal Serial Bus) was born to make it easier to connect electronic devices by using a single type of port and cable for data transfer.
Initially designed for information exchange, the USB standard has become the predominant interface for computers, smartphones, tablets, and other devices. In addition to data transfer, today’s USB technology also manages power, allowing for battery charging.
This evolution has resulted in ongoing performance enhancements, significantly increasing data transfer speeds and charging efficiency.
That said, how many types of USB ports are there?
Over the years, the USB standard has introduced various types of connectors, each with unique features related to their shape, size, and functionality. We’ll explore these in the following sections of this article!
Several USB standards are available, each distinguished by data transfer speed and power management capabilities.
Below are the main models, along with their features.
USB 2.0 was launched in 2000 and soon revolutionized the electronics industry, quickly becoming the standard connection for devices like printers, scanners, and digital cameras.
Featuring a maximum data transfer speed of 480 MB/s, USB 2.0 utilizes four wires and supports either reading or writing data, but not both simultaneously.
While faster standards have emerged, it is still widely used in many devices because of its reliability and compatibility with newer versions.
The USB 3.0 standard was born in 2008 and is an advancement over its predecessor.
With data transfer speeds reaching up to 5 Gbps—ten times faster than USB 2.0—USB 3.0 made it possible to handle large files and support more bandwidth-intensive devices.
USB 3.0 has nine wires, allowing data to be read and written at the same time, resulting in a more efficient workflow.
This standard is easily recognizable by the blue coloring of the ports and connectors.
With the introduction of USB 3.1 in July 2013, data transfer speeds reached 10 Gbps, opening up new possibilities for external hard drives, high-performance SSDs, and bandwidth-intensive peripherals. This standard further solidified USB's position as the leading interface in the industry.
The USB 3.0 standard has a complicated naming history. Introduced in 2008 as an upgrade from USB 2.0, it has undergone several renaming over the years, leading to confusion for both industry experts and consumers.
In 2013, with the launch of USB 3.1, USB 3.0 was initially rebranded as USB 3.1 Gen 1, while the new version with even higher speeds was called USB 3.1 Gen 2.
But that’s not where the story ends!
In 2019, the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) chose to update the naming convention once again, introducing USB 3.2 and renaming USB 3.1 Gen 1 and Gen 2 to USB 3.2 Gen 1 and USB 3.2 Gen 2, respectively.
This series of name changes has led to uncertainty and challenges in identifying the different versions of the standard.
Therefore, it's best to refer to data transfer speeds instead of names to clarify which USB generation is being discussed.
Officially released in 2019, USB 4.0 is the latest evolution of the standard, delivering remarkable speeds of up to 40 Gbps. This version supports Thunderbolt technology, providing exceptional performance for high-resolution video, virtual reality, and next-generation storage devices.
Moreover, USB 4.0 features more efficient power management, optimizing the energy consumption of connected devices.
When discussing USB, people often confuse the standard with the connector type.
Think of the standard as the "language" that devices use to communicate, while the connector is the "vocabulary" that provides the words of that language.
The USB standard defines the communication rules, including data transfer speeds and power delivery. In contrast, the connector is the physical component that allows devices to connect and "talk" to each other.
To illustrate the difference, consider a USB-C cable used to charge your smartphone. The connector is the oval and symmetrical part you plug into the phone. The standard, however, could be USB 2.0, 3.1, or 4.0, which determines the charging speed.
If both your smartphone and charger support USB 2.0, the charging will be slower. However, if they support USB 3.1 or 4.0, charging will occur at a faster rate.
So, even if the connector is the same (USB-C), the USB standard in use can impact performance.
Keep reading our blog, and explore the different types of USB connectors and the standards they support!
READ ALSO
Types of sockets: complete guide and features

USB Type A is the most widely used connector for peripherals like keyboards and mice. Its rectangular design has been the standard for device connections for many years. A USB Type A cable with 3.0 technology can connect to a 2.0 port, and a 2.0 cable can connect to a 3.0 port. That said, doing so will result in reduced performance.
Supported standards: USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1
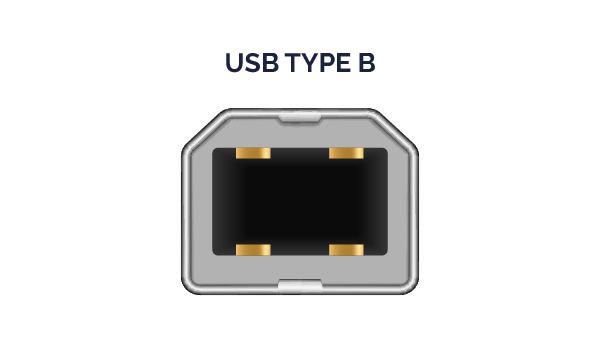
Less common than Type A, USB Type B is still widely used to connect larger devices such as scanners, printers, and specific external hard drives. It features a rectangular or square shape and manages data transfers efficiently.
Supported standards: USB 2.0, USB 3.0.

USB Type C is the evolution of previous models, featuring a compact and reversible design. It supports very high transfer speeds, fast charging, and the connection of various devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. It is progressively becoming the standard for next-generation devices.
Supported standards: USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 4.0, Thunderbolt.
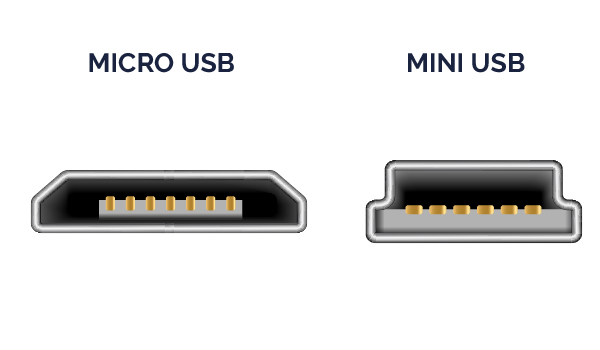
Mini-USB and Micro-USB connectors are smaller versions designed for portable devices.
Mini-USB was initially used for MP3 players and digital cameras.
Micro-USB, before the introduction of Type-C, was the standard for smartphones and tablets.
You can easily recognize USB connectors by their shapes, which vary by type.
Type A connectors are flat and rectangular, whereas Type B features a square shape and are used with printers.
Mini-USB and Micro-USB connectors are compact and feature slightly trapezoidal shapes, designed for portable devices.
READ ALSO
IP code: complete guide to the table, how to read it, and what it means
Thunderbolt and Lightning connectors are not technically classified as USB standards.
Thunderbolt, developed by Intel and Apple, uses the same design as USB Type-C and supports high-speed data transfers and power delivery, making it compatible with USB-C ports.
Lightning, on the other hand, is a proprietary connector from Apple used for devices like the iPhone and iPad, but it is not compatible with USB standards.
With the right adapters, it is possible to connect Lightning devices to USB ports.

USB 4 is the fastest port available, with data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps. It shares technology with Thunderbolt 3, making it compatible with Thunderbolt devices. USB 4 supports data transfer, video, and power delivery simultaneously.
With its versatility and impressive speed, USB 4 is rapidly becoming the go-to standard for laptops and high-performance devices.
For large buyers or companies it is possible to have price lists with different prices and payment terms.
